t-bar penetrometer|marine penetrometer testing : fabrication Full-flow penetrometers (ball and T-bar) are widely used for measurements of strength characteristics of clayey soils in offshore field investigations and laboratory tests.
WEB29 de fev. Descubra hoje no JustWatch onde você pode assistir à Liga dos Campeões, Bundesliga, Europa League e todas as outras partidas de futebol ao vivo!
{plog:ftitle_list}
5 de jul. de 2022 · Como cadastrar o currículo nas Lojas Havan - Atualizado 2022. Espero que o vídeo tenha te ajudado de alguma forma! Site oficial da HAVAN: .
t bar penetrometer simulation
The cylindrical T-bar penetrometer was developed for profiling the undrained strength of soft soils in the centrifuge and is now a widely-used . This paper provides a review of the current state of marine penetrometer deployment technology used in offshore engineering investigations and presents a summary of . In this study, the process of T-bar penetration is analyzed for the soil with strain softening. The buoyancy effect on the bearing capacity factor is studied, which shown that the .
This paper explores the interpretation of undrained shear strength and layer boundaries from T-bar penetration resistance profiles in layered soft–stiff and stiff–soft clay .
This paper describes a new analysis for the interpretation of T-bar penetrometer tests at shallow embedment and in soft soils, which is an increasingly significant consideration in the design of .
Full-flow penetrometers (ball and T-bar) are widely used for measurements of strength characteristics of clayey soils in offshore field investigations and laboratory tests. Full-flow penetrometers, ball and T-bar (Fig. 1), are widely used both in small-scale tests and field investigations in offshore engineering for measuring the shear strength of clayey sediments (Randolph et al., 2005, DeJong et al., 2010).The penetrometer is pushed into the seabed from the mudline, and the shear strength of the soil is derived from the net penetration .estimation of a T-bar test within a shallow penetration depth of 0.5D − 1.0D (D, the diameter of T-bar penetrometer), the corrections of soil strength can refer to the researches on processes of pipeline penetration (Aubeny et al., 2005; Dutta et al., 2014; Ghorai and Chatterjee, 2017). However, only a few kinds of research were
The cylindrical T-bar penetrometer was developed for profiling the undrained strength of soft soils in the centrifuge and is now a widely-used offshore site investigation tool. The conventional interpretation of the T-bar test is to convert the measured penetration resistance to soil strength using a single bearing factor associated with steady flow of soil around the bar.
The software is easy to use, and displays all the T-Bar Cone and Thruster data in real-time while recording the data for later analysis. T-Bar Cone. The T-Bar Cones are manufactured to very high physical dimensional tolerances in order to meet strict miniature cone penetrometer testing guidelines. The T-Bar Cone contains sophisticated An improved T-bar penetrometer is made and employed in laboratory to measure the undrained shear strength of the soils and its degradation with the penetration cycles. A further investigation on the microstructure of the marine soils during the cyclic penetration has been conducted. The findings indicate that there is a kind of “crust zone .
The T-bar penetrometer is a full-flow penetrometer consisting of a cylindrical bar attached perpendicularly to a set of push rods similar to those used in piezocone testing. While first used to characterize soft clays in the centrifuge (e.g., Stewart and Randolph, 1994 ), the T-bar has since been used to characterize soft clays (e.g., Low and . The T-bar penetrometer was first introduced at the University of Western Australia in order to improve the accuracy of strength profiling in centrifuge model tests (Stewart and Randolph, 1991,1994). The probe consists of a short cylindrical bar attached at right angles to the penetrometer rods, just below a load cell. It has two major . A trapped cavity above the advancing T-bar penetrometer and its influence on the corresponding bearing capacity factor are the crucial findings of this paper. The formation and evolution of the trapped cavity mechanism are studied extensively, exploring a large range of normalized undrained shear strength of soil and surface roughness of the T . Full-flow penetrometers (ball and T-bar) are widely used for measurements of strength characteristics of clayey soils in offshore field investigations and laboratory tests. However, the accuracy of the estimated undrained shear strength is hampered by: (1) the drastic variation of the bearing factor for the penetrometer at shallow and transitional penetration .
Full-flow penetration (ball and t-bar) testing is used to assess the undrained shear strength (Su) of low strength cohesive soils or mine tailings. The test incorporates a standard cone penetrometer body and a large spherical or bar attachment that replaces the standard conical tip. These penetrometers are referred to as the Ball penetration . The penetration resistance of a cylindrical T-bar penetrometer in soft clay is affected by features such as anisotropy, high strain rates, and gradual strain-softening during passage of the T-bar.
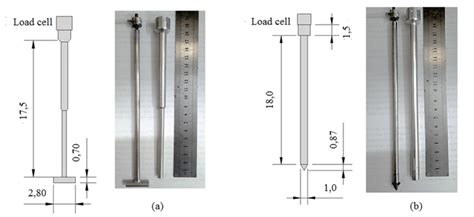
t bar penetrometer pdf
Five-layer boundary layer grids with a total thickness of D/16 and a height ratio of 1.2 are set on the outside surface of T-bar full-flow penetrometer. The grids around the T-bar are locally encrypted via the density technology from ANSYS ICEM CFD [[54], [55]]. The CFD computational domain has a total number of elements of 492,598 and a total . It seems to be promised in the use of the T-bar penetrometer in the calculation of undrained shear strength and the sensitivity of very soft organic soil for hydraulic reclamation sites. (2) For further study, more extensive tests were required to be conducted to provide the experience for determination of N T-bar by empirical methods.(hereafter CPT-10 and CPT-16, respectively), while the T-bar penetrometer (hereafter T-bar) has a tip with dimensions of 10-mm diameter by 40-mm long following the recommended length-to-diameter ratio of four (DeJong et al., 2011; Lunne et al., 2011; Chung and Randolph, 2004). The tip of the 10-mm-diameter cone penetrometer has 60° apex angle.The empirical factors established at 20 mm/s of a penetration rate for 10-mm-diameter cone, 16-mm-diameter cone and T-bar penetrometer are 18.33, 13.09 and 12.5, respectively. Undrained shear strength is a key parameter of clay and is popularly determined by penetrometers. Miniature penetrometers are preferred to estimate the und
Academic applications of the T-bar penetrometer in Brazil were conducted by Macedo (2004) in a series of field tests in the very soft grey clay of Rio de Janeiro. The results were compared with
Home; Publications; Online Library; Virtual T-bar penetrometer tests using Discrete Element Method; Publication Title Virtual T-bar penetrometer tests using Discrete Element Method The "full-flow" penetrometers (i.e., T-bar, Ball) have been widely employed in laboratory tests and in-situ investigation to determine the undrained strength profiles of fine-grained sediments in .cept that the T-bar is replaced by a sphere. Figure 1 shows T-bar and ball penetrometers with optional button filters for pore pressure measurement. A cone penetrometer with a cross sectional area of 1000 mm2 is shown for comparison of scale. Figure 1 Fugro T-bar, cone and ball penetrometers. In practice, TBT and BPT systems are compara-The cylindrical T-bar penetrometer was developed for profiling the undrained strength of soft soils in the centrifuge and is now a widely-used offshore site investigation tool. The conventional interpretation of the T-bar test is to convert the measured penetration resistance to soil strength using a single bearing factor associated with steady flow of soil around the bar. This paper .
The paper describes the first offshore application of a novel T-bar penetrometer, which overcomes some of the disadvantages of the cone penetrometer, for a site investigation in 380 m of water in the Timor Sea, off the North coast of Australia. The T-bar comprises a short cylindrical bar that is attached perpendicularly to the penetrometer rods. “FE analysis for T-bar and spherical penetrometers in cohesive soil.” In Proc., 10th Int. Offshore and Polar Engineering Conf., 617–623. Mountain View, CA: International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers (ISOPE).
An improved T-bar penetrometer is made and employed in laboratory to measure the undrained shear strength of the soils and its degradation with the penetration cycles. A further investigation on . On-site testing employing a T-bar penetrometer has become increasingly prominent for assessing DSUS strength, but the complexity of influencing parameters limits the application of this valuable method. This study utilizes a validated computational fluid dynamics (CFD) approach to model the complete process of T-bar penetration into a DSUS. Abstract. The increasing use of full-flow penetrometers for estimating the undrained and remolded shear strength as well as soil sensitivity of soft sediments by both industry and researchers has resulted in a rather rapid maturation of this new in situ test method over the past decade. Experimental, analytical, and numerical analysis results for full-flow penetrometers .
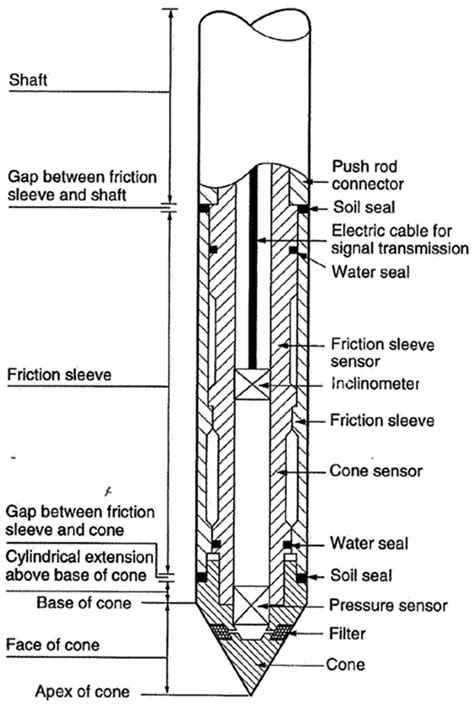
Small strain and large strain FE analyses have been carried out to detect the effects of various in-situ factors on the limiting resistance of cylindrical T-bar and spherical ball penetrometers in homogeneous cohesive soil obeying a Tresca or Von Mises failure criterion. The results confirm that the soil rigidity index has no influence on the ultimate bearing resistance for either T-bar or .
The T-bar penetrometer is a key tool to estimate the strain softening parameters by repeating penetration and extraction. In this study, the cyclic penetration process of T-bar is simulated using .
Assistir When Evil Lurks filme? Descubra onde assistir online entre 15 serviços de streaming, como Netflix, NetMovies, iTunes etc. Ver mais
t-bar penetrometer|marine penetrometer testing